Report Editor
Learn more about the Report Editor and how to configure your report for viewers.
Who can use this feature?
Users with this permission capability:
- Write Report
Not sure if you have this feature or capability? Reach out to your administrator.
The Report Editor
The Report Editor is what you will use to create and edit your reports, as shown in the following screenshot. The Report Editor allows you to enter or change the title and description of your report and insert content including subjects or events, columns, and group bys. Once you're ready to start creating reports, see Create a Report.
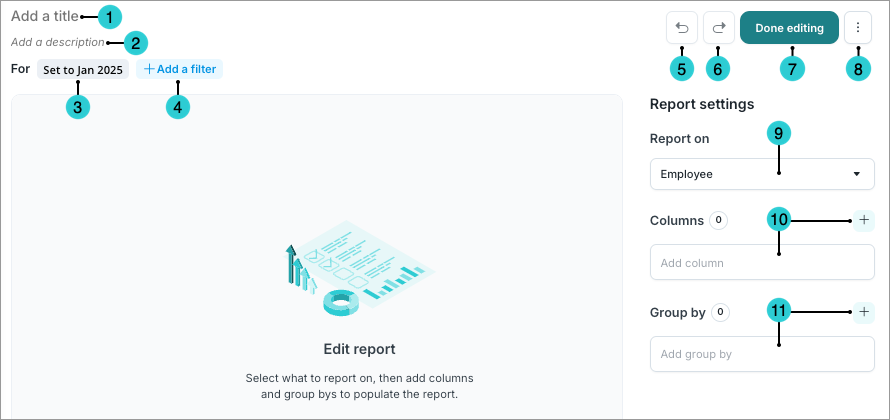
- Title box: Add a title for the report. This title appears in search results and is used in report links.
- Description box: Add a description for the report.
- Time picker: Set the time window and time context
- Add a filter: Add a filter to the entire report.
- Undo button: Undo your last action.
- Redo button: Redo your last action.
- Done editing: Close the Report Editor.
-
More options:
- Duplicate report: Make a copy of the report.
- Share report: Share the report with other users. You can select the users or user groups to give Viewer access to the report, or generate a link that you can share with other users.
Note: Users must also have the Share Analysis capability to share reports with other users.
- Delete report: Delete the report.
- Report on: Add a subject or event to report on.
- Add columns: Choose the data you want to show in columns.
- Add group by: Choose the data you want to group together in rows.
Visier’s Analytic Model and the Report Editor
Reports are built in the Report Editor using principles from Visier’s Analytic Model. For more information, see Understand Visier's Analytic Model.
Following the same principle as Visier's Analytic Model, two types of reports can be created: event-based and subject-based.
- Subject-based reports: Provide a consolidated view of data at the end of the selected time period. For example, one row will represent one employee.
Note: Subject-based reports can pull attributes from related subjects connected by a forward reference. For example, a report based on the Employee subject will have access to the Applicant subject's profile attributes.
- Event-based reports: List all the transactions that happened within the selected time period. For example, there may be multiple rows of the same employee if they have multiple recorded transactions.
Note: Event-based reports can pull attributes from related subjects. For example, a report based on the Employee Starts event will have access to the Employee subject's profile attributes.
The following attributes are available as columns in reports:
- Simple Property: Simple data stored in the data version.
- Calculated Property: A value derived from calculations performed on other attributes, including simple properties.
- Calculation Concept Property: A value derived from hierarchical calculations performed on leveled dimensions.
- Leveled Dimension: Categorical data stored in the data version.
- Selection Concept: A true or false value based on an idea that is powered by other attributes such as properties and dimensions.
- Subject Reference: A simple property, calculated property, or leveled dimension that is included from another subject. For example, a report based on Employee can include Applicant data that is pulled using a subject reference.
The following attributes are available as group by's in reports:
- Dimension: Attributes that classify data and differentiate one data record from another.
- Leveled Dimension
- Parent-Child Dimension
- Range Dimension
- Subject Reference Dimension: A dimension that is included from another subject.
The following filters are available in reports:
- Selection Concept: True or false statements that organize data into groups, meaning that if the criteria is met, it is true, and if not, it is false.
- Dimension Member: The values of a dimension. For example, Chicago is a dimension member on the Location leveled dimension.
